- No products in the cart.
Mini Titrator for Measuring Titratable Acidity in Dairy Products
Mini Titrator for Measuring Titratable Acidity in Dairy Products
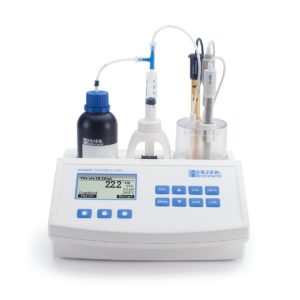
The HI84529 is an easy to use, fast and affordable automatic mini titrator designed for testing titratable acidity levels in dairy products. Based on an acid-base titration method, this mini titrator uses an optimized pre-programmed method of analysis with a powerful algorithm that determines the completion of the titration reaction by the use of a specialized foodcare pH electrode.
The HI84529 incorporates a precision piston style dosing pump that adjusts the volume of dosing dynamically based on the voltage change. This dosing system reduces the amount of time required for the titration while providing for a highly accurate determination of the amount of titrant used.
This mini titrator is supplied complete with all the materials necessary to perform low and high range measurements of titratable acidity. All chemicals are premixed and prepackaged including standardized titrants, reagents and pump calibration solution. There is no need for volumetric glassware or analytical balances.
- Piston driven pump for accurate dynamic dosing
- Complete with anti-clogging reference electrode
- Pre-standardized titrant and pre-measured reagents
Mini Titrator for Measuring Titratable Acidity in Dairy Products
The HI84529 uses methods based on AOAC International and Standard Methods for the Examination of Dairy Products. Both of these methods report titratable acidity as % lactic acid and a conversion factor is used to convert the results to the other available units. The HI84529 can be customized to meet the needs of any dairy analysis lab. Samples can be titrated by weight or volume, diluted or non-diluted (low range only) and titrated to a fixed pH endpoint that can be adjusted by the user. The HI84529 offers three different methods depending on the expected range and the weight of sample used. Select low range 50 to titrate a 50 mL or 50 g undiluted sample. The other titration options are low range 20 and high range 20 to titrate 20 mL or 20 g samples that are diluted twice their volume with deionized or distilled water.
There are two fundamentally different measurements of dairy products: titratable acidity and pH. pH is a measurement of hydrogen ion concentration while titratable acidity is the neutralizing capacity of a dairy product with NaOH. An increase in acidity can be caused by bacteria formation. Monitoring acidity is a way of determining the quality and freshness of dairy products. Acidity is determined by a pH endpoint titration using NaOH (sodium hydroxide), and is defined as the consumption necessary to shift the pH value from 6.6 (corresponding to fresh milk) to a pre-determined pH value. When using phenolphthalein as an indicator, a faint pink color change occurs at pH 8.3.
Titratable acidity is expressed in a variety of units based on the titration method performed. Each method varies in sample size and strength of NaOH used for the titration.
% Lactic Acid (%l.a.): Determined by taking a 20 mL or 20 g sample and diluting with twice its volume with deionized or distilled water. The sample is then titrated with 0.1 M NaOH to a phenolphthalein endpoint.
Degree Soxhlet Henkel (°SH): Determined by titrating a 50 mL sample with 0.1 M NaOH to a phenolphthalein endpoint.
Degree Dornic (°D): Determined by titrating a 100 mL sample with N/9 NaOH to a phenolphthalein endpoint.
Degree Thörner: Determined by taking a 10 mL sample and diluting with twice its volume with deionized or distilled water. The sample is then titrated with 0.1 M NaOH to a phenolphthalein endpoint.
Knowing the relationship between sample weight or volume and strength of titrant it is possible to convert the reading obtained from one method to another. Below is a table with the factors preprogrammed in the HI84529 for converting between various units of measure.
Characteristics:
| Range | Low Range: %l.a.: 0.01 to 0.20; °SH: 0.4 to 8.9; °D: 1.0 to 20.0; °Th: 1.1 to 22.2 High Range: %l.a.: 0.1 to 2.0; °SH: 4.4 to 88.9; °D: 10 to 200; °Th: 11.1 to 222.2 |
| Resolution | Low Range: %I.a.: 0.01 ; °SH: 0.1; °D: 0.1; °Th: 0.1 High Range: %I.a.: 0.1; °SH: 0.1; °D: 1; °Th: 0.1 |
| Accuracy (@25ºC/77ºF) | Low Range: ± 0.01 %l.a. High Range: ± 0.1 %l.a. |
| Sample Volume | LR 20: 20 mL or 20 g LR 50: 50 mL or 50 g HR 20: 20 mL or 20 g |
| Methods | acid base titration |
| Principle | endpoint titration, adjustable (pH 8.0 – 8.7 in 0.1 increments) |
| Pump Speed | 10 mL/min |
| Stirring Speed | 800 (Low Range) / 1000 (High Range) |
| pH Range | -2.0 to 16.0 pH; -2.00 to 16.00 pH |
| pH Resolution | 0.1 pH / 0.01 pH |





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.